다단연소사이클 액체 로켓엔진의 압력제어에 대한 연구
Copyright ⓒ The Korean Society of Propulsion Engineers
This is an Open-Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
초록
나로우주센터에 구축/개발된 3단 엔진 연소시험설비에서 다단연소사이클 액체 로켓엔진의 시험을 수행하였다. 수류시험과 점화시험, 연소시험이 이루어졌으며 예연소기의 연소압력 제어를 위한 TTR의 개도를 143°에서 185°까지 변화시키며 시험을 수행하였다. 시험 결과 엔진의 주요성능과 TTR 개도에 의한 수력학적 변화를 확인하였지만 연소압력의 제어성 확인을 위한 결과는 얻지 못하였다. 향후 본 논문의 연구에서 도출된 개선점을 보완한 예연소기 압력제어 연구가 이루어질 것이다.
Abstract
For the control of pre-burner combustion pressure, the open angle of the TTR (Throttle for Thrust Regulation) valve was varied from 143° to 185° while testing cold flow, ignition, and combustion. The major performance variables of rocket engines and hydraulic performance of the TTR valve regarding the open angle were verified. However, the controllability of pre-burner combustion pressure was not verified due to the limitations of the test. Comprehensive research will be done after addressing these problems.
Keywords:
Staged Combustion Cycle, Powerpack, Preburner, Liquid Rocket Engine키워드:
다단연소사이클, 파워팩, 예연소기, 액체로켓엔진1. 서론
한국형발사체 KSLV-II 이후의 발사체에는 보다 많은 유상하중과 높은 임무궤도 진입을 위해 재점화가 가능한 고성능의 고공엔진이 요구된다. 이를 위하여 다단연소사이클 액체로켓엔진을 개발하여 성능을 높이고자 연구가 수행되고 있다[1-20]. 예연소기를 중심으로 한 각 부분품에 대한 개발연구[1-15]와 연소기가 없는 파워팩 시험이 고흥항공센터에서 수행되었으며[16,17] 현재 나로우주센터 3단 엔진 연소 시험설비에서 개선된 Schematic을 적용한 개발시제품을 이용한 연구가 수행되고 있다[18-20]. 본 논문의 연구에서는 예연소기(Pre-burner)의 압력제어를 위한 유량제어밸브의 개도변화에 따른 엔진 성능변수의 변화에 대하여 분석하고자 한다.
2. 시험 설비 및 시험대상체
2.1 3단 엔진 연소 시험설비
3단 엔진 연소 시험설비는 액체산소와 케로신을 추진제로 이용하는 액체로켓용 연소기를 최대 10 tonf까지 시험할 수 있다. Fig. 1에 시험설비의 개략도를 나타내었다. 평시에 저장 중이던 산화제/연료를 시험 시에는 저장탱크에서 런탱크로 충전을 하여 엔진 시험조건에 맞도록 터보펌프 입구압력을 맞추기 위해 런탱크를 기체질소를 이용하여 가압을 하게 된다. 런탱크와 엔진사이의 배관경로가 실제 발사체보다 길기 때문에 시동조건을 모사하기 위한 시동탱크가 런탱크와 엔진 테스트스탠드 사이에 위치하며 시험내용에 따라 활용하게 된다[21].
2.2 시험대상체
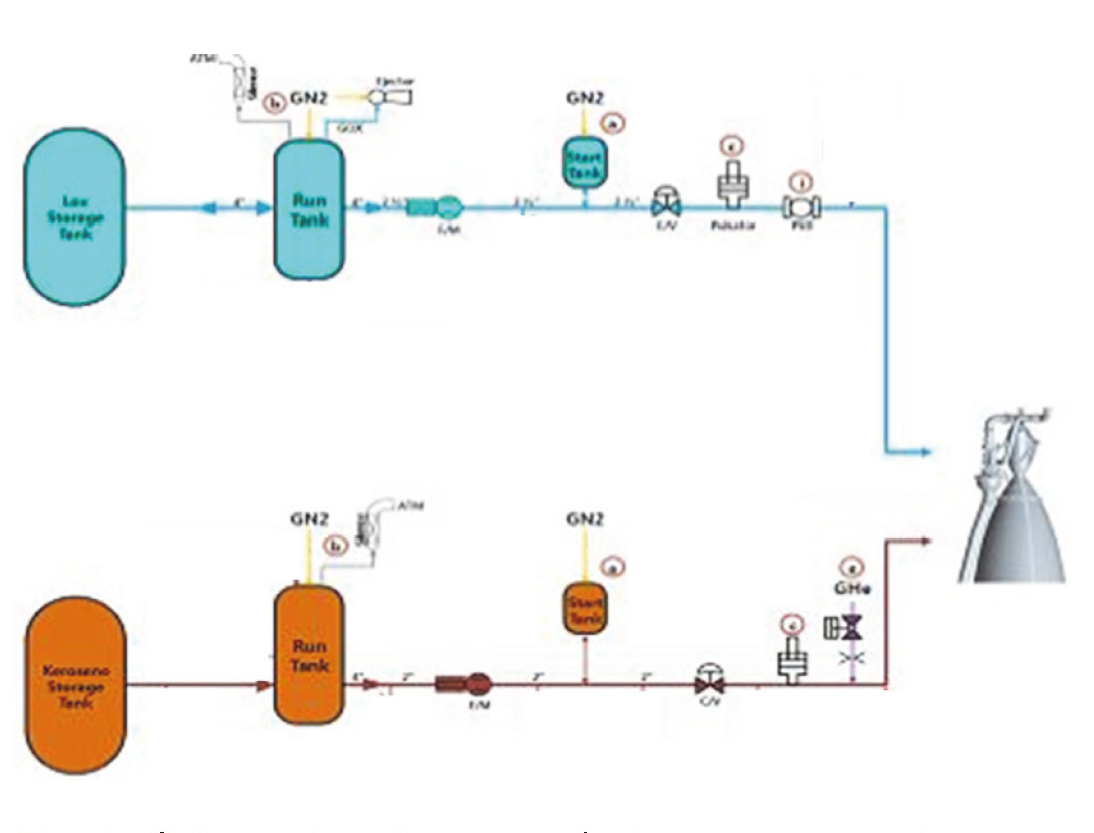
Fig. 2에 시험대상체인 다단연소사이클 액체로켓엔진의 시스템 개략도를 나타내었다. 본 논문의 연구의 주제로 삼고 있는 로켓엔진의 압력제어는 Fig. 2에 노란색으로 강조한 부분이 핵심적인 역할을 하게 된다.
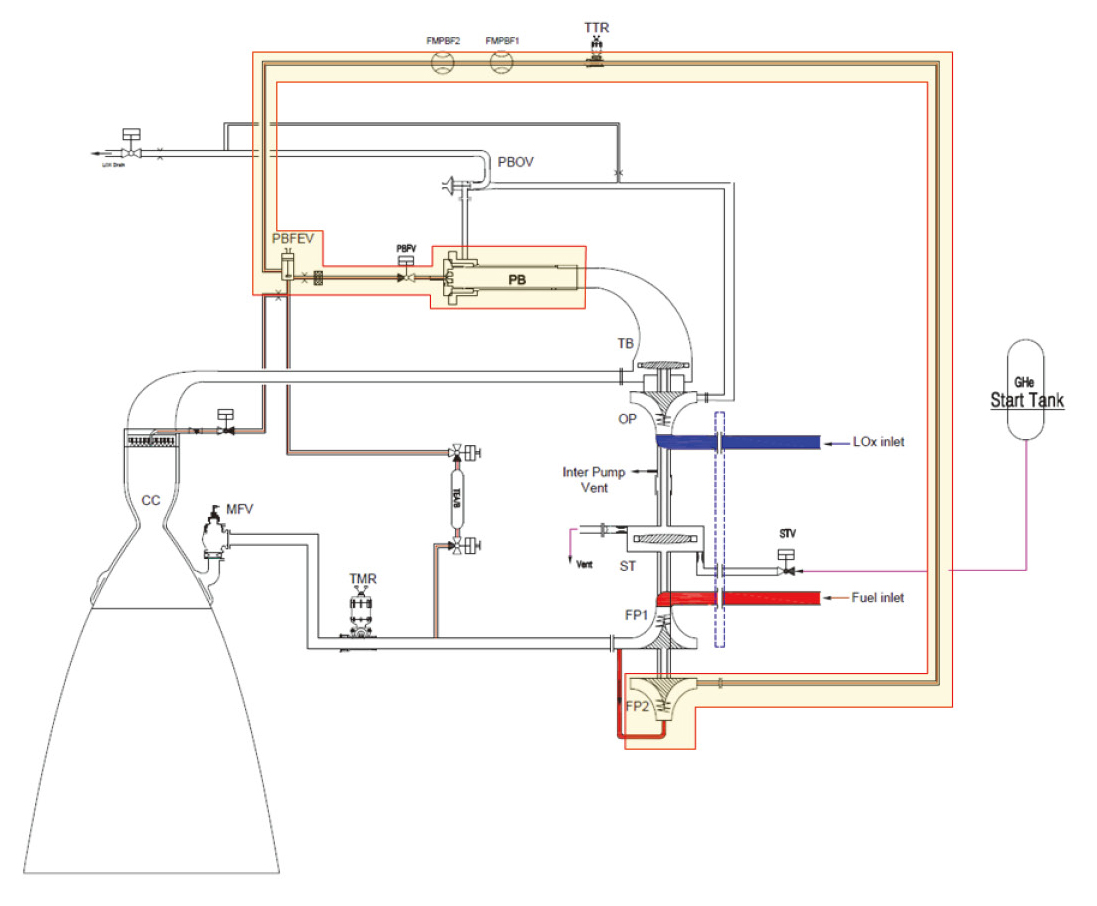
Schematic diagram of staged combustion liquid rocket engine. (yellow highlighted section: = pressure control schematic of system).
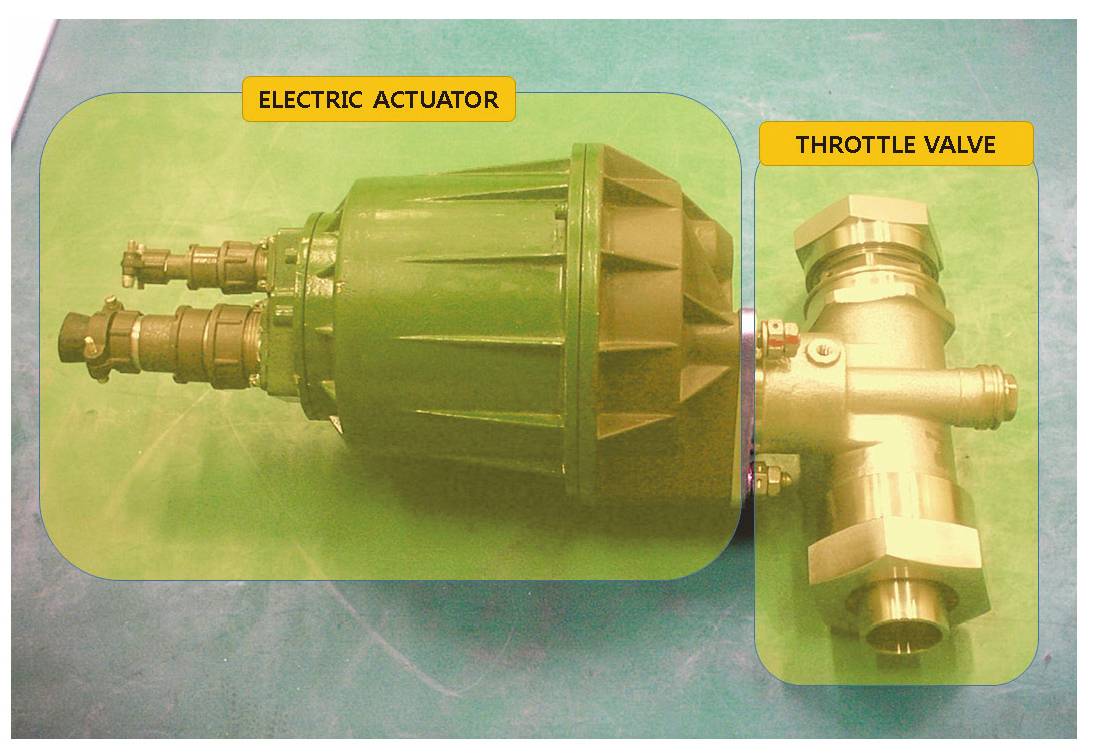
다단연소 액체로켓엔진의 연료펌프는 2단계로 나누어져 있으며, 1단 펌프를 지난 연료가 2단 펌프를 통해 한단계 더 승압된 후 터보펌프 동력발생을 위한 예연소기(Pre-burner)로 공급되게 된다. 2단 연료펌프와 예연소기 사이에 Fig. 3에 나타낸 유량제어밸브 TTR(Throttle for Thrust Regulation)이 위치하게 되는데 이것이 다단연소사이클 엔진의 압력제어를 위한 핵심 구성품이다.
이 로켓엔진은 예연소기에서 발생된 산화제과잉 연소가스가 터빈동력을 발생시킨 후 연소기로 공급되어 최종적으로 추력을 발생시키게 된다. 따라서 예연소기에서 연소반응에 참여하는 연료인 케로신의 공급량에 따라 터보펌프 동력 및 로켓엔진의 추력이 조절된다.
3. 시험 결과
시험은 크게 다음의 세 가지로 분류하여 수행하였다.
- 1. 예연소기의 점화가 없이 고압헬륨을 이용한 시동터빈 구동 수류시험 2회
- 2. 시동터빈 구동 후 짧은 예연소기 점화시험
- 3. 시동터빈 구동 후 예연소기 점화하여 10초 이상 연소시험 2회
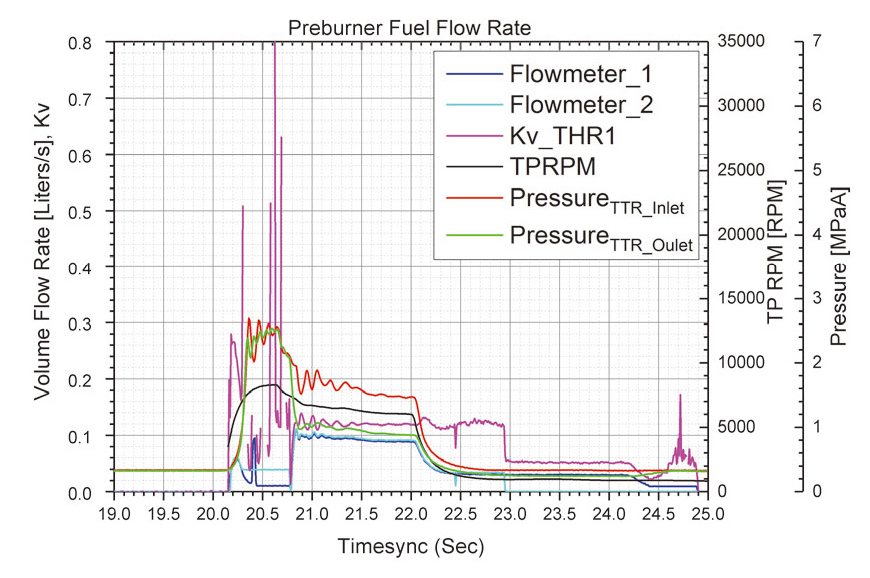
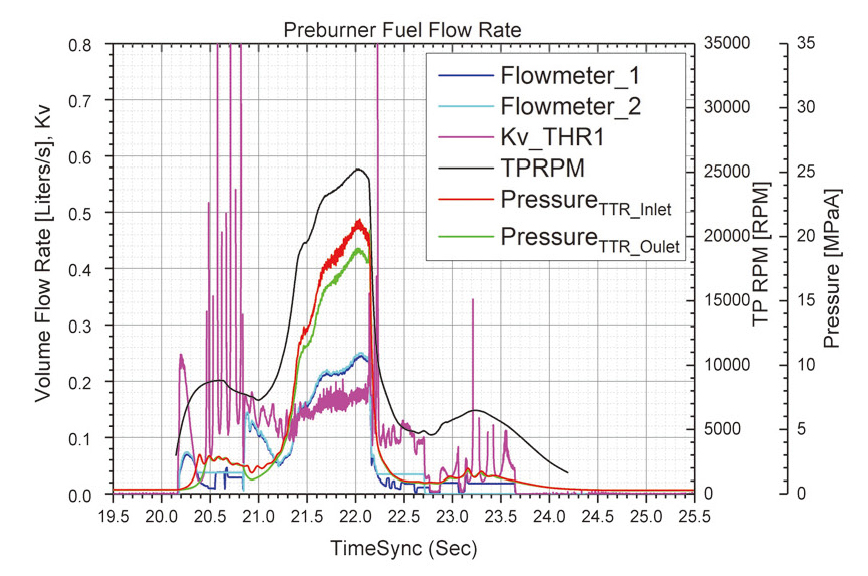
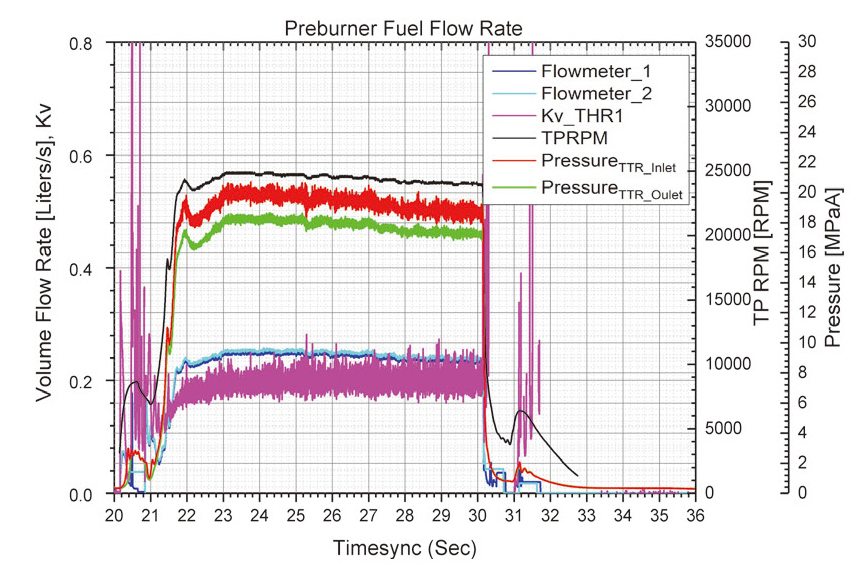
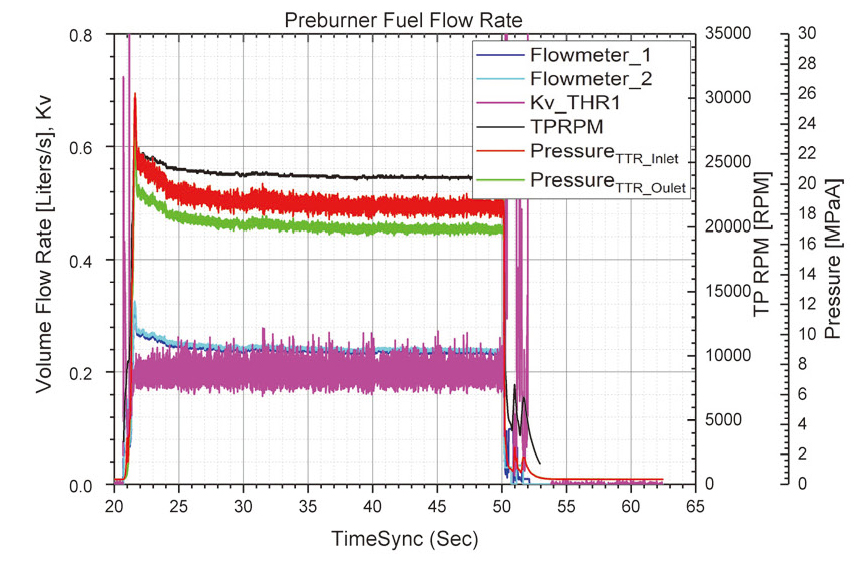
위의 시험을 하는 동안 TTR 의 개도는 143°, 172°, 185°로 변화시켜 유량과 Kv 를 확인하고자 하였다. Fig 4-8에 각 시험을 통해 얻어진 결과 그래프를 나타내었으며 정상상태에 도달한 구간의 값을 평균을 내어 Table 1과 같이 분석하였다. 점화 없이 시동터빈만을 구동했던 수류시험 ①, ②에서는 TTR 개도를 각각 143°, 172° 로 설정하였고 이에 따라 예연소기로의 연료공급 유량이 0.326 m2/h에서 0.359 m2/h으로 늘어났다. 이 때 TTR 의 Kv는 각각 0.120, 0.153이었다.
점화시험에서는 정상상태 구간이 존재하지 않아 예연소기에 연료가 공급되어 연소가 일어난 22.055 초의 데이터를 데이터 분석을 위해 제시하였다. 점화시험의 TTR 개도는 수류시험 ②와 동일한 172°였지만 예연소기 점화로 인한 터빈동력이 발생하여 터보펌프 RPM 과 유량이 크게 차이가 나며 이로 인해 TTR 전후의 차압과 Kv 가 다른 결과를 보였다.
점화시험과 연소시험 ①의 결과를 비교해보면 TTR 의 개도 증가에 따라 Kv 값은 증가 하였지만 유량과 터보펌프 RPM 은 점화시험에서의 값이 더 높은 것을 확인할 수 있다. 이는 점화시험 분석시점은 점화초기 터보펌프 RPM이 overshoot하여 연소시험 ①, ② 정상상태보다 1000 RPM 이상 높게 터보펌프가 작동하였기 때문이다. 같은 시험조건으로 시간을 늘렸던 연소시험 ②의 결과는 연소시험 ①의 결과와 동일하다.
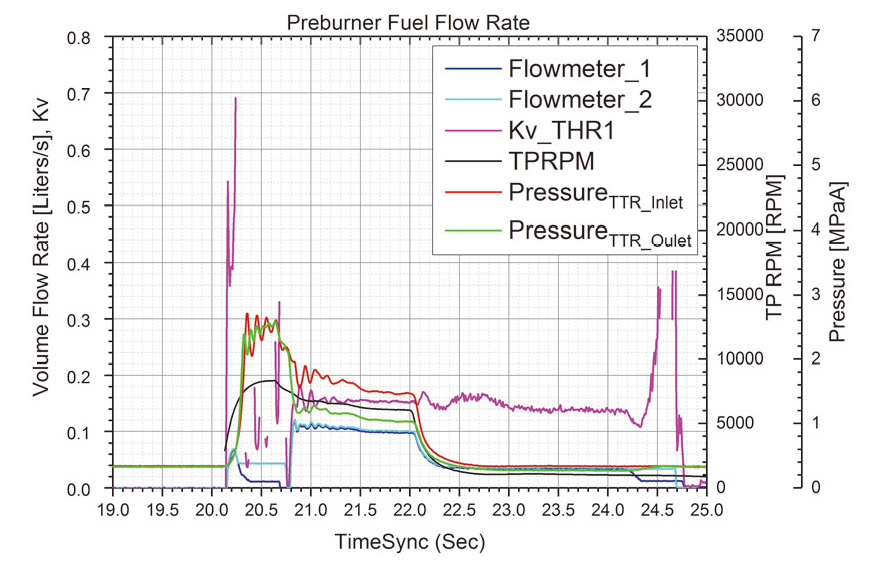
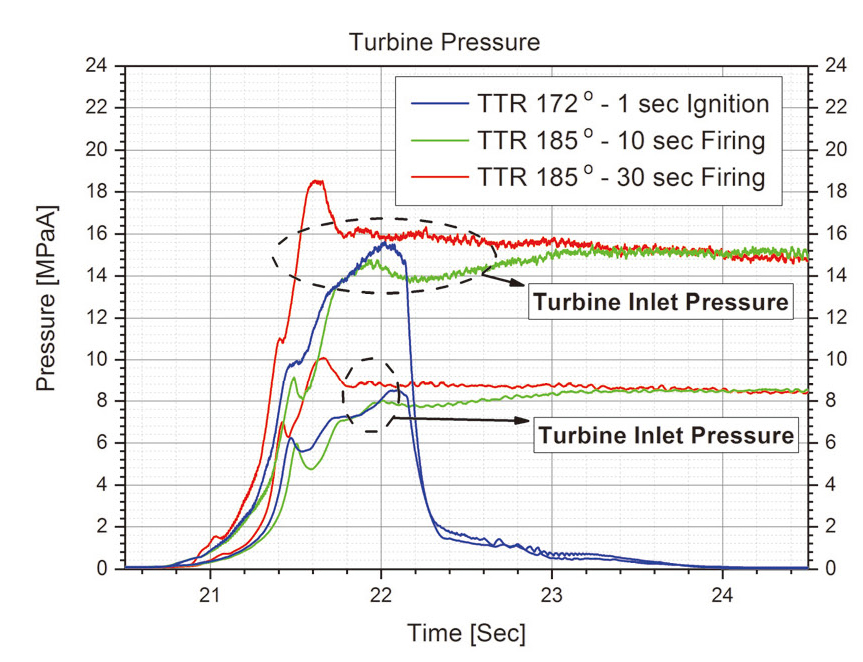
본 논문의 연구의 목적은 TTR 의 개도를 변화시켜 예연소기로의 연료공급량을 조절, 예연소기의 연소압력 제어하고자 함이다. 따라서 예연소기의 압력을 측정해야 정확한 비교가 되겠지만 예연소기 제작상의 이유로 현재의 시험대상체에서는 측정하지 못하였다. 따라서 예연소기의 후단인 터빈 입/출구 압력의 결과를 Fig. 9의 그래프에서 비교하였다.
20.5-22.0초 구간에 각 시험의 터빈입구압력이 형성되는 경향성이 모두 다른데 이는 아직 점화시퀀스가 안정되지 않았기 때문이다. 따라서 TTR의 개도가 같았던 연소시험 ①, ②의 터빈 입/출구 압력이 시동구간 이후 정상상태 구간에서 같음을 확인하였을 뿐, 점화시험과 연소시험에서 TTR의 개도가 달라짐에 의한 터빈 입/출구 압력비교는 현 시점에서는 어렵다고 판단된다.
4. 결론
한국항공우주연구원 나로우주센터 내의 3단 엔진 연소 시험설비에서 다단연소사이클 액체 로켓엔진의 연소시험을 수행하였다. 시험은 수류시험과 점화시험, 연소시험으로 순차적으로 이루어졌으며 예연소기의 연소압력 제어를 위한 TTR의 개도를 143°에서 185°까지 변화시키며 시험을 수행하였다.
시험 결과 개도가 증가할수록 TTR 유량제어밸브를 통한 유량과 Kv 값이 증가함을 확인하였지만 점화시점의 천이구간 거동, 점화시퀀스의 변동에 따라 달라지는 압력상승 거동 변화로 인해 정확한 성능 비교가 어려웠다. 이에 향후에는 시동구간에서 재현성 있는 압력형성 경향을 보일 수 있도록 점화시퀀스를 안정화 하는 연구의 필요성을 확인할 수 있었다.
향후의 연구에서 다단연소사이클 액체 로켓엔진의 압력제어에 대한 명확한 성능분석을 하기 위해서는 각기 다른 TTR 개도에서 정상상태에 도달한 연소시간을 확보한 시험이 수행되어야 한다. 또한 현재 예연소기의 압력을 직접 측정할 수 없었는데 이를 다음 예연소기 시제에는 제작단계에 반영하여 엔진 성능과 직결된 예연소기 압력을 직접 측정해야 할 것이다. 이러한 개선을 통해 최종적으로는 연소시험 중 TTR의 개도를 변화시켜 실시간으로 엔진의 성능을 제어할 수 있는 연구가 진행될 것이다.
Acknowledgments
이 논문은 한국추진공학회 2017년도 춘계학술대회(2017. 5. 31-6. 2, 라마다프라자 제주호텔) 발표논문을 심사하여 수정 ․ 보완한 것임.
References
- Yang, J.H., So, Y.S., Choi, H.K., Choi, S.M., and Han, Y.M., "An Experimental Study of the Rocket Preburner Injector", Proceeding of the 2006 KSPE Fall Conference, Sunchon, Korea, p47-53, Nov), (2006.
- So, Y.S., Yang, J.H., Choi, S.M.,, Kwon, K.C., and Han, Y.M., "An Experimental Study of the Spray Characteristics for the Oxidizer-rich Preburner Injector", Proceeding of the 2006 KSAS Fall Conference, Busan, Korea, p988-994, Nov), (2006.
- Yang, J.H., So, Y.S., Han, Y.M., Yoon, Y.B., and Choi, S.M., "Spray Characteristics of the Rocket Preburer Injector", Proceedings of 2007 ILASS-Korea Conference, Yeosu, Korea, p109-113, Oct), (2007.
- So, Y.S., Yang, J.H., and Choi, S.M., "Spray Characteristics of the Oxidizer-rich Preburner Injector in Ambient Pressure Environment", Proceeding of the 2007 KSPE Spring Conference, Seoul, Korea, p97-101, Apr), (2007.
- So, Y.S., Yang, J.H., Choi, S.M., and Han, Y.M., "Spray Characteristics of the Oxidizer-rich Preburner Injector in Ambient Pressure Environment", 9th Space Launch Technology Symposium, Busan, Korea, p16-17, Jan), (2008.
- Yang, J.H., and Choi, S.M., "Spray Characteristics of the Oxidizer-rich Preburner Injector in High Pressure Environments", Journal of the Korean Society of Propulsion Engineers, 12(2), p48-56, (2008).
-
Shin, J.C., Jung, T.K., and Lee, S.Y., "Simulation of Pre-burner Performance in Liquid-fueled Rocket Engine for Satellite Launch Vehicle", Journal of The Korean Society for Aeronautical and Space Sciences, 36(12), p1180-1185, (2008).
[https://doi.org/10.5139/JKSAS.2008.36.12.1180]
- Kim, J.K., Han, Y.M., Bae, T.W., Choi, H.S., and Yoon, Y.B., "Spray Characteristics of Gas-centered Swirl Coaxial(GCSC) Injector in High Pressure Condition", Proceeding of the 2010 KSPE Fall Conference, Jeju, Korea, p5-8, Nov), (2010.
- Moon, I.S., and Shin, K.C., "Numerical Study of the Cooling Channel of the Preburner for a Small Liquid Rocket Engine", Proceeding of the 2010 KSPE Spring Conference, Seoul, Korea, p21-24, May), (2010.
- Jeon, J., Hong, M., Han, Y.M., and Lee, S.Y., "Experimental Study on Spray Characteristics of Gas-Centered Swirl Coaxial Injectors", Journal of Fluids Engineering, 133(12), p121303-1-121303-7, (2011).
- Moon, I.Y., Moon, I.S., Yoo, J.H., Jeon, J.H., Lee, S.M., Hong, M.G., Ha, S.U., Kang, S.H., and Lee, S.Y., "Ignition Test of an Oxidizer Rich Preburner", Proceeding of the 2011 KSPE Fall Conference, Busan, Korea, p869-872, Nov), (2011.
-
Kim, J.G., Han, Y.M., Choi, H.S., and Yoon, Y.B., "Study on spray patterns of gas-centered swirl coaxial (GCSC) injectors in high pressure conditions", Aerospace Science and Technology, 27, p171-178, (2013).
[https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ast.2012.08.004]
-
Seo, S.H., Kang, S.H., and Lee, S.Y., "Study on Pressure Fluctuations Observed in Combustion of Oxygen-Rich Preburners", Journal of the Korean Society of Propulsion Engineers, 17(2), p122-127, (2013).
[https://doi.org/10.6108/KSPE.2013.17.2.122]
- Moon, I.S., Moon, I.Y., and Ha, S.U., "Study on Starting Procedures for Staged Combustion Cycle Engines", Proceeding of the 2013 KSPE Spring Conference, Busan, Korea, p95-98, May), (2013.
- Kim, S.Y., Moon, I.S., Ha, S.U., and Moon, I.Y., "Ignition Test of a Small Preburner", Proceeding of the 2014 KSPE Spring Conference, Seoul, Korea, p21-24, Ma), (2014.
- Kim, D.K., Ha, S.U., Moon, I.Y., Moon, I.S., Lee, S.Y., Ji, S.Y., and Seo, J.W., "Construction of Firing Test Facility for 8tonf Class Staged Combustion Cycle Rocket Engine", Proceeding of the 2015 KSPE Spring Conference, Busan, Korea, p835-838, Ma), (2015.
- Ha, S.U., Kim, D.K., Moon, I.Y., Moon, I.S., and Lee, S.Y., "Powerpack Test of Staged-combustion Cycle Rocket Engine with Kerosene and Liquid Oxygen", Proceeding of the 2016 KSPE Spring Conference, Jeju, Korea, p309-314, Ma), (2016.
- Lee, J.H., Woo, S.P., Jeon, J.S., Seo, D.B., Kim, C.H., Lee, K.J., Yoo, B.I., and Han, Y.M., "Configuration of Turbopump and Hydraulic lines of Staged Combustion Cycle Engine", Proceeding of the 2016 KSPE Fall Conference, Jungsun, Korea, p944-947, Dec), (2016.
- Woo, S.P., Lee, K.J., Lee, J.H., Im, J.H., Jeon, J.S., Hwang, C.H., and Han, Y.M., "The Design of Technology Demonstration Model for Tests of Staged Combustion Cycle Engine", Proceeding of the 2016 KSPE Fall Conference, Jungsun, Korea, p934-937, Dec), (2016.
- Jeon, J.S., Lee, J.H., Woo, S.P., Im, J.H., Lee, K.J., Yoo, B.I., Cho, N.K., and Han, Y.M., "The Ignition System of a Staged Combustion Cycle Engine", Proceeding of the 2016 KSPE Fall Conference, Jungsun, Korea, p1055-1058, Dec), (2016.
- Kim, S.H., Jung, Y.G., Wang, S.W., So, Y.S., and Han, Y.M., "Development of 3rd Stage Engine Test Facility for KSLV-II Propulsion System", Proceeding of the 2013 KSPE Fall Conference, Busan, Korea, p451-455, Ma), (2013.